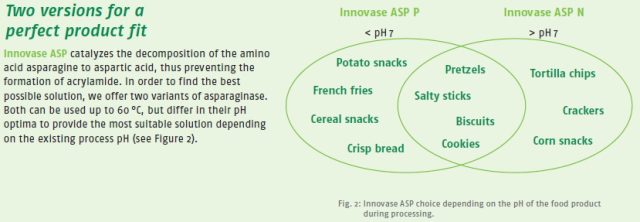
Innovase ASP
Key features
- Efficient acrylamide reduction
- Only minor process or recipe adjustments
- Unchanged taste and texture of the end products
- Applicable to a wide range of products
Description
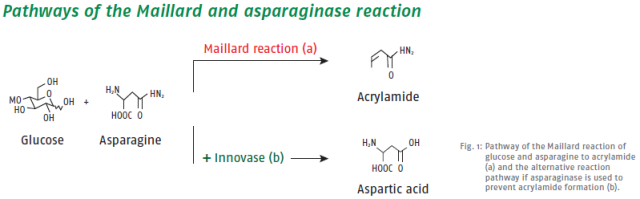
The formation of acrylamide is a result of the Maillard reaction between reducing sugars and asparagine, a naturally occurring amino acid. Unfortunately, acrylamide is suspected of being a potential carcinogen and is thus considered a process contaminant. This has led to almost worldwide regulations to reduce acrylamide in food products. Proven mitigation strategies usually include drastic changes in process conditions and raw material selection, both of which risk undesirable changes in product properties. Innovase ASP, on the other hand, removes asparagine from the Maillard reaction with little, if any, process adjustments (see Fig. 1).